What is Volcanic Smog (AKA Vog)? Is Vog Dangerous? [Health Effects of Vog]
What is Volcanic Smog?
Volcanic smog, also known as vog, is a form of air pollution caused when sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide emitted from a volcano react with oxygen and water particles in the air.
The resulting mixture of airborne pollutants can penetrate deep into the lungs and irritate the tissues and mucus membranes of the eyes, nose and throat. Vog is colorless smoke that can have harmful health effects on those who breathe it in over time. It can also cause eye irritation due to its ability to reflect sunlight back into the eyes of those exposed to it.
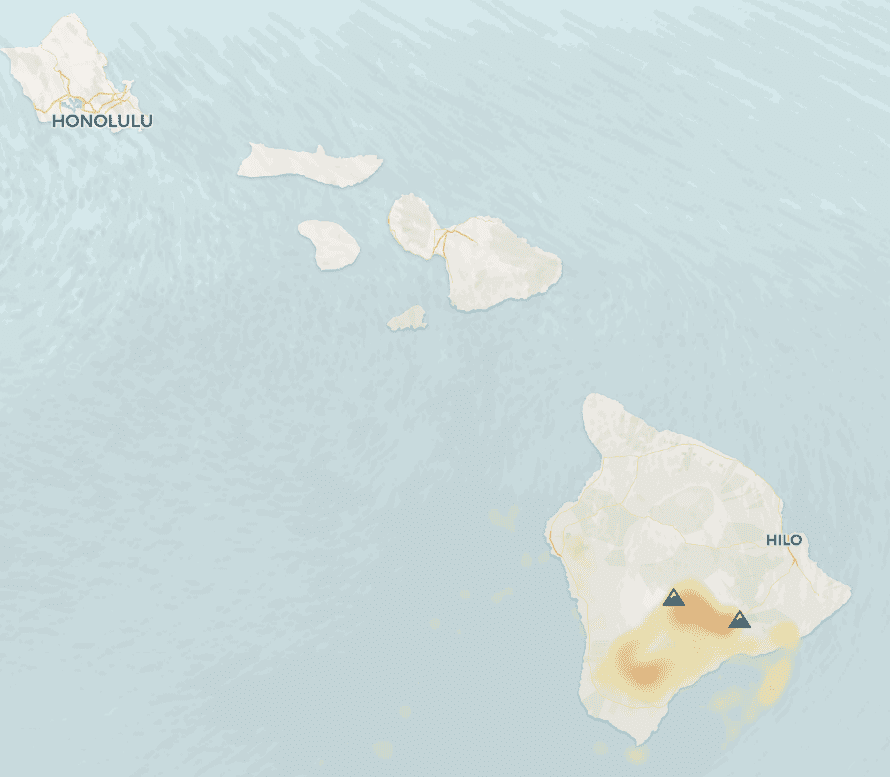
Big Island Hawaii Vog Tracker
The VMAP Vog Forecast Dashboard displays information on near-surface air quality from volcanic gas emissions. The VMAP forecasts are intended to (1) provide guidance on the location/envelope of the vog plume; and (2) provide guidance on the locations of possible health risks for general public, as defined by the EPA. All products, data and graphics provided on the VMAP website are for general information purposes only. Default animation controls are displayed in viewer’s local time.
What are the Health Effects of Vog?
1. Lung Problems
Lung problems caused by vog include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Headaches
- Irritated lungs and throat
- Dry coughs and difficulty breathing
2. Headaches
Headaches caused by vog can be due to irritation and coughing, as well as fatigue and dizziness. Other possible symptoms include:
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Difficulty concentrating
- Insomnia or sleep disturbances
- Muscle pain or aches
The headaches caused by vog are a direct result of exposure to the volcanic gases released into the air. The gases contain sulfur dioxide (SO2), which is a toxic gas that can cause irritation of the respiratory system when inhaled in high concentrations. This leads to coughing and difficulty breathing, which can lead to fatigue and dizziness if prolonged exposure continues.
3. Irritated Eyes
The irritant effects of vog on the eyes include burning, itching, wateriness and soreness. It can also lead to inflammation of the eyelids or conjunctivitis. Symptoms such as blurred vision, difficulty focusing and light sensitivity may also occur.
4. Throat Irritation
The symptoms of throat irritation caused by vog include burning eyes, runny noses, sore throats, headaches and sinus pressure. You may also experience fatigue and dizziness if you come into contact with vog and feel out of breath or abnormally tired.
5. Difficulty Breathing
The symptoms of difficulty breathing in response to vog may include: chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue and dizziness. If you come into contact with vog and experience any of these symptoms, seek medical help immediately as it could be a sign that your pre-existing medical condition has been exacerbated by the vog exposure.
6. Asthma Symptoms
Asthma symptoms of vog include: irritation and coughing, fatigue, dizziness, difficulty breathing or out of breath feeling, chest pain or tightness in the chest. Other symptoms may include headache, runny nose, sore throat and sinus pressure.
7. Skin Irritation
The skin irritation health effects of vog include: burning eyes, runny noses, sore throats, headaches and sinus pressure. It can also cause dry skin and itchy patches of skin. In extreme cases, vog exposure may lead to skin infections such as bacterial infections or fungal infections such as athlete’s foot or ringworm.
8. Drops in Oxygen Levels
Vog is a type of air pollution caused by volcanic emissions. It contains high levels of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and other toxic gases, as well as particulate matter such as ash particles.
When these harmful substances enter the atmosphere, they can affect oxygen levels by reducing the amount of available oxygen in the air. This can cause breathing difficulties, induced asthma attacks in adolescents, increased susceptibility to respiratory ailments and impeded ability of the respiratory tract to remove other potentially harmful particles. It may also lead to headaches, watery eyes and sore throats. Long-term effects are unknown but vog may cause you to experience more severe issues such as chest pain and shortness of breath in those who have pre-existing medical conditions.
9. Exposure to Chemicals and Gases
Chemicals and gases present in vog include sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, hydrochloric acid and particulate matter. Sulfur dioxide is the main component of vog, accounting for up to 90% of its composition. Other gases present include hydrogen sulfide (rotten egg smell), carbon monoxide and nitric oxide. Additionally, hydrochloric acid can be produced when sulfur dioxide reacts with water vapor in the atmosphere. Particulate matter includes dust particles from volcanic eruptions as well as aerosols such as ash or soot from burning vegetation after a volcanic eruption has occurred.
10. Increased Risk of Pneumonia
Vog is a type of air pollution caused by volcanic eruptions. It contains sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and other toxic gases that can be inhaled into the lungs.
These gases can irritate the lungs, causing inflammation and weakening of the respiratory system. This increases the risk of developing pneumonia or other respiratory diseases, such as bronchitis or asthma.
How to Protect Yourself From Vog’s Health Effects?
1. Avoid areas with high concentrations of vog
1. Familiarize yourself with key air monitoring websites and the SO 2 and PM 2.5 advisory codes/levels.
2. Be aware of winds that could carry vog to your area, and keep track of when it may affect you locally.
3. If vog will be heavy in your area, take extra precautions—especially if you suffer from a chronic breathing problem such as asthma or COPD (which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema).
4. Do not smoke; avoid secondhand smoke; stay indoors; use an air conditioner if possible; keep it on recirculation setting; have medications handy if needed (and instructions from physician); assume lung condition may worsen during periods of vog; contact physician as soon as problems develop!
You can find out the wind direction by watching television weather reports or listening to weather radios – they usually provide spatial information regarding which areas are affected by vog!
2. Use air-purifying devices
Using air-purifying devices can help protect you from the health effects of vog by removing the dangerous airborne chemicals, gases, particles, and toxic metals associated with volcanic smog. These specially designed air cleaners feature a custom blend of deep-bed activated carbon for enhanced adsorption of toxic pollutants and medical-grade filtration for fine particles.
By using these devices in your home or workplace, you can reduce your exposure to harmful pollutants associated with volcanic smog and decrease your risk of health complications such as respiratory problems or irritation of the eyes, throat and lungs.
3. Use masks to prevent inhaling vog particles
Masks can help protect against vog particles by providing a barrier between the wearer’s lungs and the harmful gases and particles in the air.
Wearing a mask can reduce exposure to vog particles by limiting outdoor physical exertion, preventing secondhand smoke inhalation, blocking out indoor pollutants such as smoking candles/incense, and keeping doors and windows closed to limit exposure to outside air. Additionally, an appropriate air-cleaning device can help reduce SO 2 and PM2.5 levels in indoor areas with doors or windows closed.
4. Check the weather forecasts and stay indoors during vog episodes
1. Stay informed about vog levels in your area by monitoring weather reports, listening to a weather radio, or checking the weather section of your local newspaper.
2. Be aware of wind conditions that could carry vog to your area and adjust your activities accordingly to avoid exposure when necessary.
3. Drink plenty of fluids unless you have a medical condition that requires you to limit fluid intake; avoid physical exertion if you have breathing problems; and don’t count on dust masks for protection as they may not fit well or provide adequate protection from smaller particles during vog episodes.
4. Ask about oxygen use if applicable and consult with a physician before adjusting levels of intake if needed (Call before taking any action).
5 Understand key air monitoring websites/codes/levels used for volcanic haze so that you know what precautions need to be taken during periods of heavy vog exposure (e..g., staying indoors with an air conditioner on recirculation setting).
5. Close windows and curtains to keep indoor air clean
Closing windows and curtains can help protect from vog’s health effects by reducing the amount of sulfur dioxide, acid gases, and other particulates that are able to enter your home. This will limit your exposure to these harmful substances and decrease your risk of experiencing adverse health effects such as respiratory issues or skin irritation. Additionally, running an air conditioner or dehumidifier will condense water out of the indoor air, further removing particulate sulfur compounds from your environment.
6. Limit outdoor activities
Limiting outdoor activities can help protect you from vog’s health effects by reducing your exposure to the harmful sulfur particles and acid gases it contains. Avoiding high vog level areas, staying indoors with windows and doors closed and sealed, avoiding physical activity when vog levels are high, running an air conditioner or dehumidifier to condense water out of the indoor air, using a fan with a towel draped over it to neutralize particles; all of these actions will reduce your exposure to vog and its associated health risks. Additionally, staying hydrated, refraining from smoking or tobacco use and following your doctor’s advice can help ensure optimal health during periods of high vog levels.
7. Use indoor plants to remove vog from the air
1. Check air quality levels daily to determine if the vog levels are high enough to warrant using indoor plants to remove it from the air.
2. As a family, make a plan so that everyone knows what to do and where to go when vog levels are high.
3. When possible, avoid high VOG level areas and stay indoors with windows and doors closed and sealed.
4. Run an air conditioner or dehumidifier; both will condense water out of the indoor air, removing particulate sulfur compounds and acid gases from your indoor air..
5 . To increase their effectiveness , use fan with a hand towel or piece of cheesecloth saturated in baking soda paste draped over its face at low/medium speed..Keep cloth damp at all times but be careful not get fan motor wet..
8. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated
Drinking plenty of water can help protect you from vog’s health effects by keeping your body hydrated and reducing the risk of fatigue. Additionally, drinking water can help flush out toxins in your body and reduce the risk of respiratory issues caused by vog.
9. Keep an eye on the symptoms of vog-related health problems and seek medical attention if needed
The symptoms of vog-related health problems include irritation, coughing, fatigue, dizziness and shortness of breath. If you come into contact with vog and start to feel out of breath or abnormally tired, it is important to seek shelter indoors immediately and keep all doors and windows tightly closed. If these symptoms persist or worsen at any point, it is important to visit a doctor for further evaluation.
To monitor your health when living near vog sources, pay attention to how you feel physically over time. If you start experiencing any of the abovementioned symptoms or others that are out of the ordinary for you, seek medical help right away so that any potential issues can be identified and addressed quickly.
10. Stay informed about vog developments and updates
1. Get familiar with key air monitoring websites and the SO 2 and PM 2.5 advisory codes/levels.
2. Be aware of winds that could carry vog to your area and keep track of any changes in wind conditions that could affect its reach.
3. Keep medications handy if you have asthma or other respiratory conditions; call your doctor if you need them but don’t already have them available on hand.
4. Stay informed about vog developments and updates by following local news outlets, visiting air monitoring websites frequently, or signing up for alerts from organizations such as the Hawaii State Health Department (SHD).
Good Vog Side Effects
One of the only good side effects of vog is that it makes for amazing sunset pictures:





